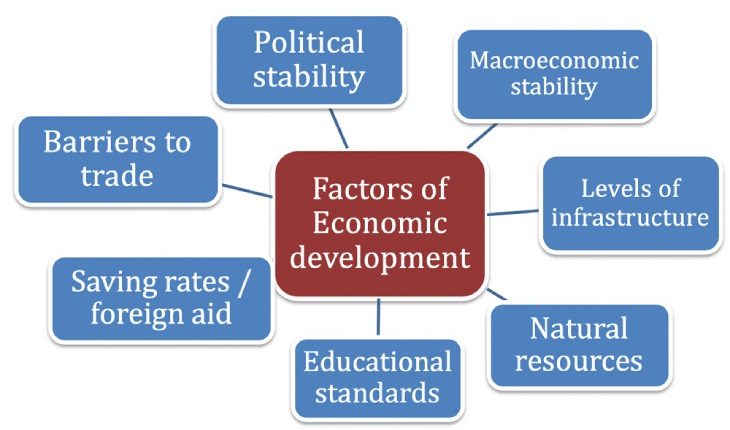
The Great Depression Might Just Be Around Corner
It was in the 1930s, the United States raised high tariffs that triggered a currency war leading to the great depression. There is now a similar condition as US President Donald Trump has threatened to levy 10% tariffs on the $300 billion import from China that was not subject to any levies so far. The two countries have been in constant war to show dominance and power. China could very well manage this by manipulating the currency in gaining supremacy in the trade war.
China’s attempt to let the Chinese yuan devalue past 7$ will help the country counteract the tariff levied by the US on Chinese goods. This act could send market tumbling all over the globe. As the relationship between the two countries, US and China, continue to deteriorate, the investors and market seem to weaken against the trade war. This is not a good news as the international economy could plummet to the bottom making the world a poor and dangerous place to live. The US and China could face extreme downturn while other countries might experience collateral damages. There are no winners in the trade war. If the tariffs remain permanent, so are the economic losses.
Read More About : Coronavirus And International Economy
Crisis Leading To Dwindling International Economy
Emerging economies have always attracted investors. It could be due to ease of doing business or currency management. They mostly offer faster growth and strong returns. There are investments that have been happening outside the global power. These emerging economies are easily vulnerable to changing economic conditions. Factors like strong US dollar, global trade tensions, rising interest rates will pose challenges to most of the emerging markets. Currency crisis can be a huge challenge for emerging markets like Armenia, Mexico, Brazil, South Africa and Turkey.
Developing economies feel the financial panic and strain of weak policymaking, external imbalances and political instability. This will lead to a full blown currency crisis leading to a banking crisis that will slow down the pace of economic development. If the crisis remains constant, investors can eventually abandon emerging markets around the globe making way for a fragile international economy.

Environmental risks and climate crisis are also a few factors that can affect the international economy. It is the most uncertain factor as extreme climatic conditions can lead to unprecedented events leading to decrease in agricultural output, rebuilding of nations, loss of industries and more. Drought and floods could lead to destruction of resources and increase climate related costs. Regions prone to frequent climate crises find themselves with a weak economy.
Brexit And Other Factors
The United Kingdom’s departure from the European Union is still shrouded with uncertainty. The fact that the country’s economy has decreased by 0.2% could very well lead the UK to a recession in ten years. The country has been constantly facing negative growths due to the general uncertainty, devaluation of stocks, falling foreign investments and shutdown of manufacturing companies. Economists around the world expect Brexit could lead to a weaker economy, political fragmentation and a less efficient international dialogue.
Before the European Union, all the nations in Europe represented a small but open economy. But even a large European Union as a closed economy is also attractive with tightly knit regions providing easy service and regulatory norms.
Data fraud and cyber attacks are other factors leading to a crisis in the international economy. Numerous data breaches can affect millions of people. Cyber attacks on public organizations and private institutions are now frequent occurrences that cause damage to data triggering huge loss. Cyber crime cost the world $5 trillion annually.